Exposing gRPC Services Using TCM
Background
gRPC is a long-connection service, and load imbalance is common with long-connection services. When using layer 4 load balancing, load balancing can only occur at connection scheduling level but not at request level. Different connections may have varying request counts, network traffic, request latency, and connection duration, easily causing different Pod loads. Istio naturally supports gRPC load balancing at layer 7, forwarding different requests to different backends to avoid load imbalance. Tencent Cloud Container Service has productized istio, called TCM. This article introduces how to use TCM to expose gRPC services.
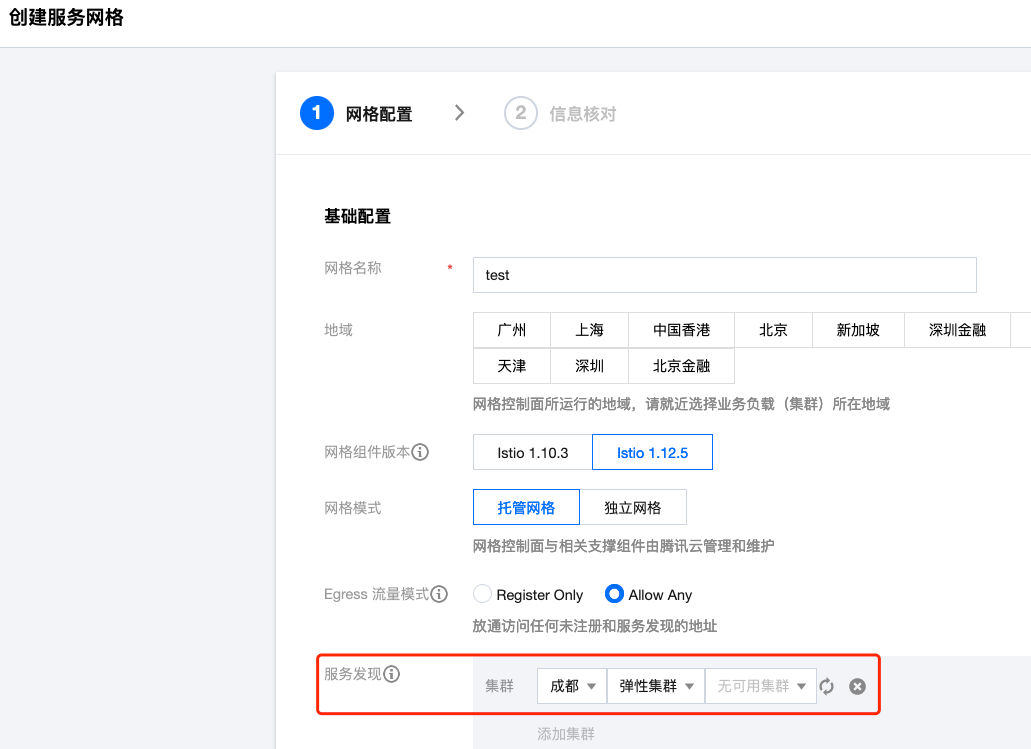
Creating Mesh
Go to TCM Console, create a new mesh. Each mesh can manage multiple TKE/EKS clusters, associate clusters during mesh creation (or associate later):
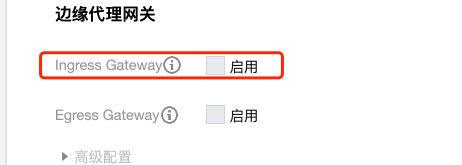
Edge proxy gateway usually enables Ingress Gateway, exposing internal services via CLB:
Enabling Sidecar Auto-injection
After mesh creation, enter it, in 【Services】-【Sidecar Auto-injection】, check namespaces to enable auto-injection:
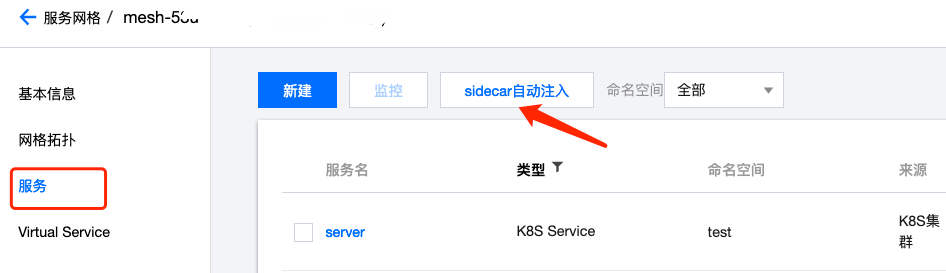

Check namespace where gRPC server is deployed.
Deploying gRPC Server
Deploy gRPC service to one cluster in mesh, ensure deployment namespace has sidecar auto-injection enabled:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: server
namespace: test
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: server
spec:
containers:
- name: server
image: docker.io/imroc/grpc_server:latest
imagePullPolicy: Always
If server was deployed before enabling auto-injection, recreate server Pods - recreation triggers auto-injection.
Creating Service
Associate Service with workload, create using yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: server
namespace: test
labels:
app: server
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 8000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 50051
name: grpc
selector:
app: server
Note:
- Key point: port name must start with grpc, or directly write grpc - istio identifies protocol type via port name.
- Not creating via console mainly because console Service creation doesn't support specifying port names.
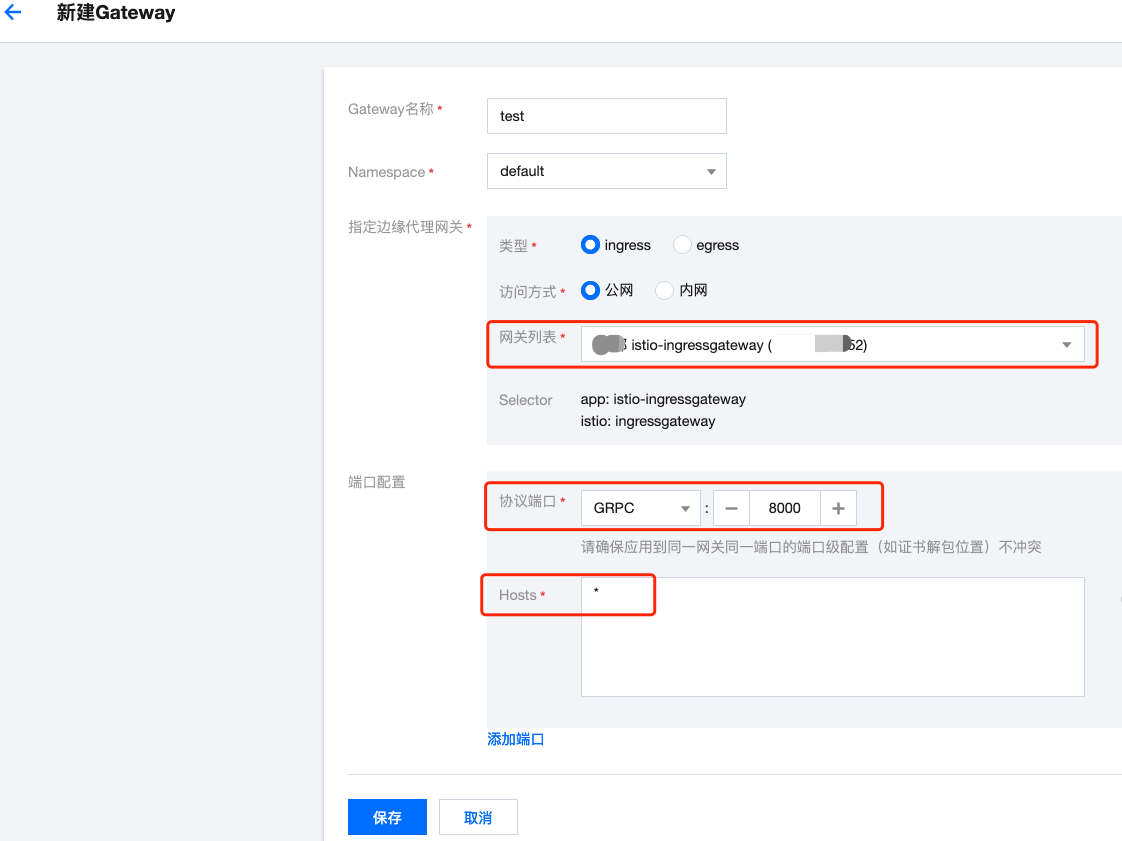
Creating Gateway
If gRPC needs external cluster exposure, istio requires Gateway object. If not created, create one first. In TCM: 【Gateway】-【New】:

【Gateway List】 references initially created Ingress Gateway, 【Protocol Port】 uses GRPC, specified port number is CLB listener port, 【Hosts】 is IP or domain for external service access, wildcard * matches all:
Creating VirtualService
VirtualService is istio's basic object describing services. Use VirtualService to associate gRPC service with Gateway for external exposure. In TCM: 【Virtual Service】-【New】:
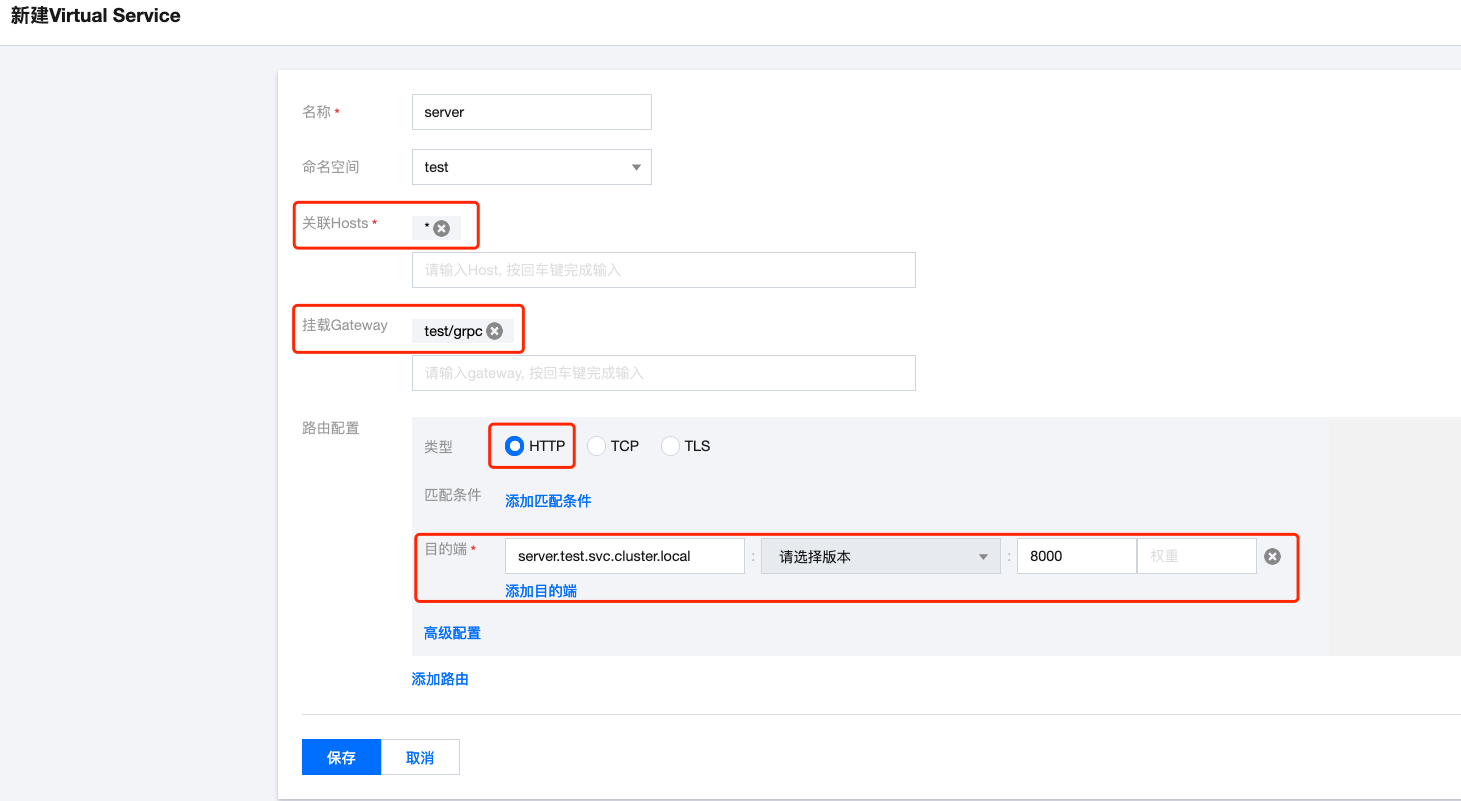
【Name】 arbitrary, 【Namespace】 server's namespace, 【Associated Hosts】 can match Gateway settings, 【Mount Gateway】 select previously created Gateway, 【Type】 select HTTP (istio's http can route both http and grpc), 【Match Conditions】 delete defaults, no conditions, 【Destination】 select server's service + port:
Save, then gRPC service can be accessed via CLB exposed address, with automatic request-level load balancing. CLB address depends on created Ingress Gateway's CLB. Test effect:

If creating Virtual Service via yaml, reference example below:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: server
namespace: test
spec:
gateways:
- test/grpc
hosts:
- '*'
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: server
Demo Repository
Contains server code examples, Dockerfile, deployment yaml, etc.
Repository: https://github.com/imroc/grpc-demo