Enabling CLB Direct Pod Access
Overview
TKE provides CLB direct pod access capability, bypassing NodePort and shortening the network path by one hop, bringing several benefits:
- Shorter path, potentially improving performance.
- No SNAT, avoiding issues like source port exhaustion and conntrack insertion conflicts that may occur with concentrated traffic.
- No NodePort bypass means no k8s iptables/ipvs forwarding, converging load balancing state to CLB alone, avoiding global load imbalance caused by dispersed load balancing state.
- Natural real source IP acquisition without needing
externalTrafficPolicy: Localsince there's no SNAT. - Simpler session persistence implementation - just enable session persistence on CLB without setting Service's
sessionAffinity.
Although CLB direct pod access offers many benefits, it's not enabled by default. This article explains how to enable CLB direct pod access on TKE.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster version must be higher than 1.12, as CLB direct binding to Pods requires checking if Pod is Ready beyond just Running status and readinessProbe, also requiring LB health checks on Pods, which depends on the
ReadinessGatefeature introduced in Kubernetes 1.12. - Cluster network mode must enable
VPC-CNIelastic network interface mode, as current LB direct pod access implementation is based on elastic network interfaces. Regular network modes are temporarily unsupported but may be supported in the future.
CLB Direct Pod Access Enablement Methods
Enablement is achieved by declaring the use of direct access mode when creating Service or Ingress.
Service Declaring CLB Direct Pod Access
When exposing services using LoadBalancer-type Service, declare using direct mode:
- If creating Service through console, check
Use LoadBalancer Direct Pod Mode:

-
If creating Service via yaml, add annotation
service.cloud.tencent.com/direct-access: "true"to Service:apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
service.cloud.tencent.com/direct-access: "true" # Key point
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx-service-eni
spec:
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- name: 80-80-no
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: LoadBalancer
CLB Ingress Declaring CLB Direct Pod Access
When exposing services using CLB Ingress, also declare using direct mode:
- If creating CLB Ingress through console, check
Use LoadBalancer Direct Pod Mode:
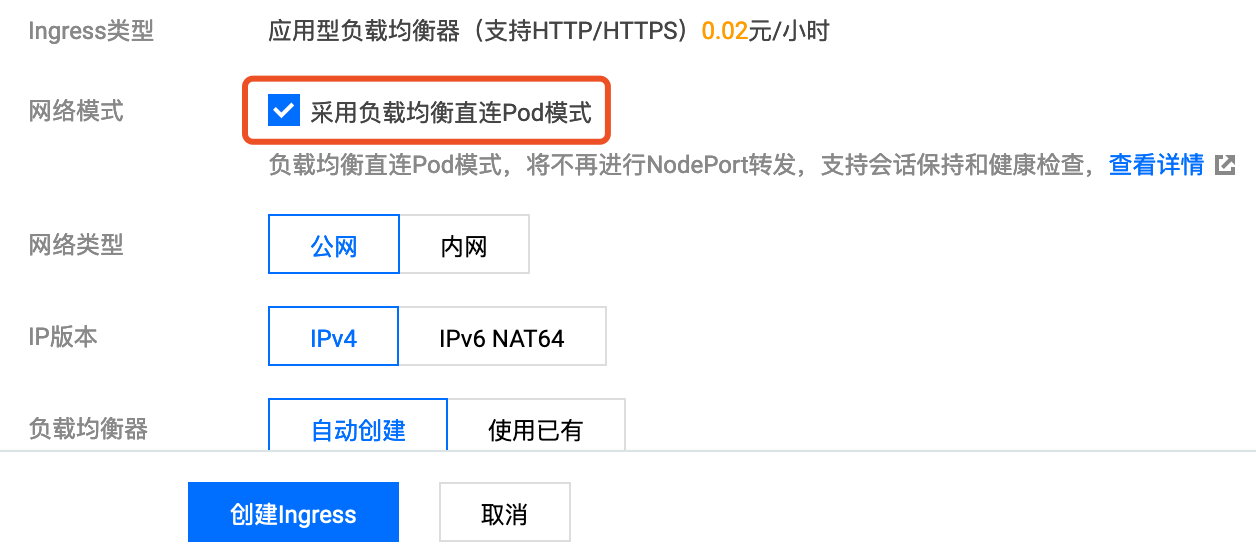
-
If creating CLB Ingress via yaml, add annotation
ingress.cloud.tencent.com/direct-access: "true"to Ingress:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
ingress.cloud.tencent.com/direct-access: "true"
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: qcloud
name: test-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: nginx
servicePort: 80
path: /
Enablement methods have slight differences based on cluster network mode, explained below.
GlobalRouter + VPC-CNI Network Mode Mixed Usage Notes
If TKE cluster was created with GlobalRouter network mode and later enabled VPC-CNI, the cluster uses mixed GlobalRouter + VPC-CNI network modes.
Pods created in such clusters don't use elastic network interfaces by default. To enable CLB direct pod access, first declare that Pods should use VPC-CNI mode (elastic network interfaces) when deploying workloads. Specific method: use yaml to create workloads (not through TKE console), specify annotation tke.cloud.tencent.com/networks: tke-route-eni for Pod to declare using elastic network interface, and add tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip: "1" requests and limits to one container. Example:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx-deployment-eni
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
annotations:
tke.cloud.tencent.com/networks: tke-route-eni
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
resources:
requests:
tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip: "1"
limits:
tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip: "1"