Using Traefik Traffic Gateway on TKE
Overview
Traefik is a modern cloud-native reverse proxy tool that offers significant advantages over Nginx:
- Supports three traffic management configuration methods simultaneously: Kubernetes Ingress API, Traefik CRD, and Gateway API.
- Provides a feature-rich Dashboard management interface supporting visual route configuration and monitoring.
- Deeply integrates with Prometheus to provide complete Metrics data for monitoring and alerting.
- Supports rich traffic governance features including: multi-version canary releases, traffic mirroring, automatic Let's Encrypt HTTPS certificate issuance, flexible middleware mechanisms, etc.
This article describes how to deploy Traefik in TKE clusters and manage traffic through various configuration methods.
Installing Traefik
- Search for
traefikin the TKE Application Market. - Click
traefikto enter the application details page. - Click Create Application.
- Suggested application name:
traefik, select the target cluster where Traefik should be installed.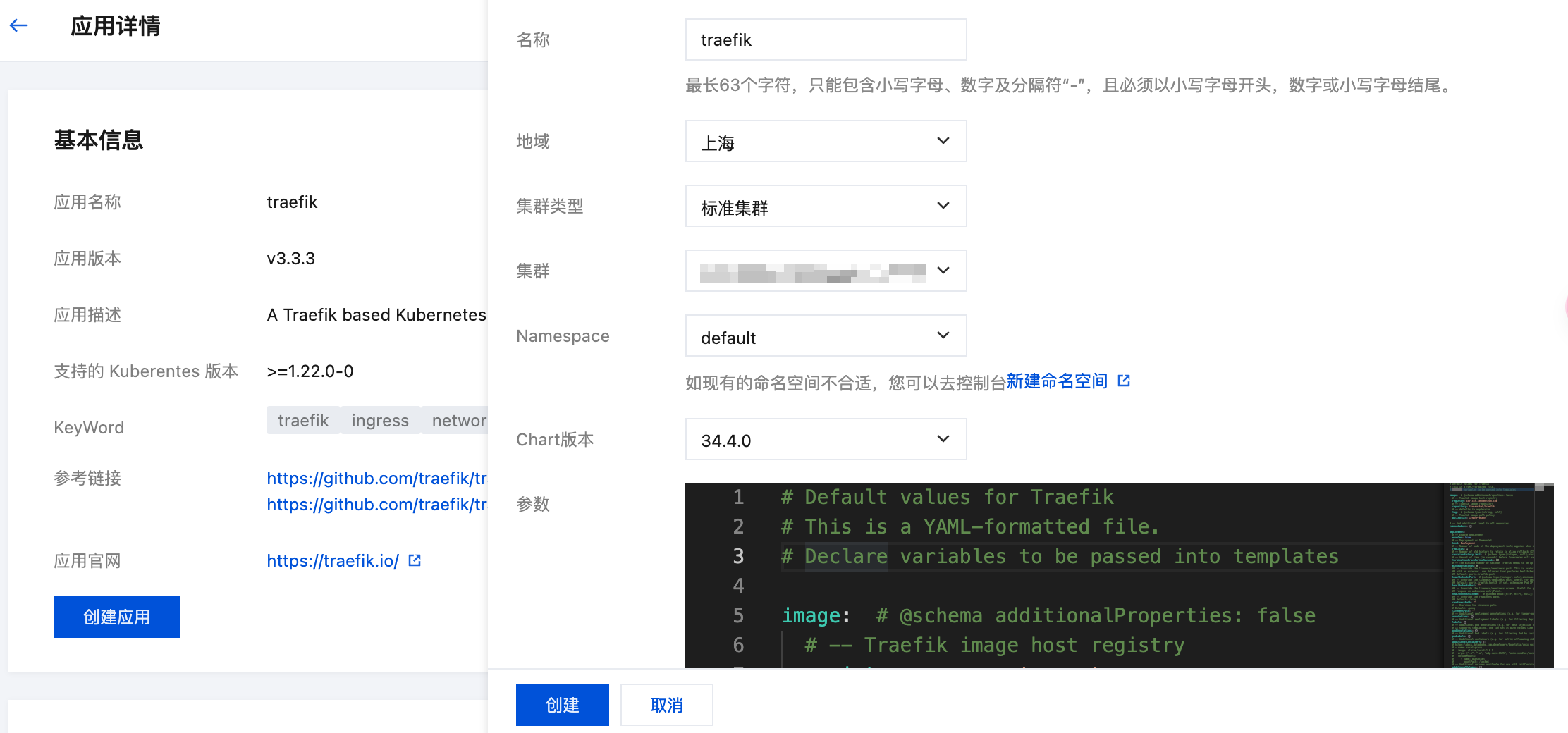
- Refer to the Traefik Parameter Configuration section below, configure parameters according to requirements, then click Create to install Traefik into the cluster.
- After installation, find the Traefik application in Application Management, click the application name to enter the details page, and check the CLB address information in the Service section. Configure DNS resolution for the domains you need to use, ensuring domains resolve to Traefik's CLB address.
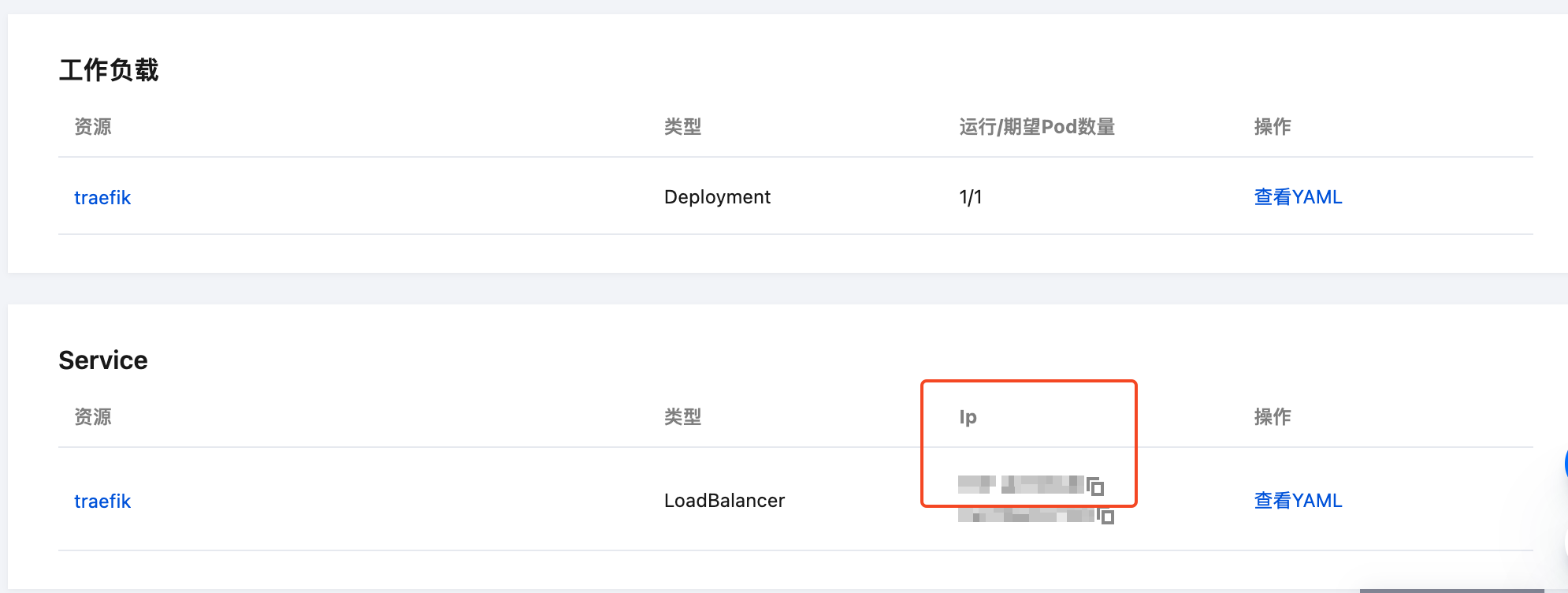
If you need to modify configurations later, find the Traefik application in Application Management, click Update Application and edit parameters.
Traefik Parameter Configuration
Here are some parameter configuration recommendations for installing Traefik, which can be modified according to requirements.
This article uses the TKE Application Market to install Traefik. Applications installed via the TKE Application Market are Helm charts, where the Traefik application is sourced from the open-source community's traefik-helm-chart. Parameter configuration (values.yaml) is completely consistent with the community (except for image addresses). If you install via Helm, you can also refer to the parameter configuration suggestions here.
Enable CLB Direct-to-Pod
It's recommended to enable CLB direct-to-pod, so CLB can forward traffic directly to Pods without going through NodePort, reducing latency. Traefik itself can perceive the real source IP, and backend business Pods can obtain the real source IP through headers.
For more details, refer to Using LoadBalancer Direct-to-Pod Mode Service.
Configuration method:
service:
annotations:
service.cloud.tencent.com/direct-access: "true"
Use Existing CLB
If you already have a CLB created, you can specify the CLB instance ID:
For more details, refer to Service Using Existing CLB.
Replace lb-xxx with your existing CLB instance ID.
service:
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/tke-existed-lbid: lb-xxx
Public and Private Network Simultaneous Access
By default, a public CLB is created. You can achieve simultaneous access via both private and public CLBs with similar configuration:
Automatic creation of private CLB requires specifying subnet ID, replace subnet-xxxxxxxx.
- Auto Create
- Use Existing CLB
ports:
web:
expose:
default: true
internal: true
websecure:
expose:
default: true
internal: true
service:
additionalServices:
internal:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/qcloud-loadbalancer-internal-subnetid: "subnet-xxxxxxxx" # 配置内网 CLB 的子网
You need to create the private CLB yourself, obtain the instance ID and replace lb-xxx in the configuration.
ports:
web:
expose:
default: true
internal: true
websecure:
expose:
default: true
internal: true
service:
additionalServices:
internal:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/tke-existed-lbid: lb-xxx
IPv4 and IPv6 Simultaneous Access
By default, an IPv4 CLB is created. You can achieve simultaneous access via both IPv6 and IPv4 CLBs with similar configuration:
For more details, refer to Using IPv6 on TKE.
- Auto Create
- Use Existing CLB
ports:
web:
expose:
default: true
ipv6: true
websecure:
expose:
default: true
ipv6: true
service:
additionalServices:
ipv6:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/service.extensiveParameters: '{"AddressIPVersion":"IPv6FullChain"}'
You need to create the IPv6 CLB yourself, obtain the instance ID and replace lb-xxx in the configuration.
ports:
web:
expose:
default: true
ipv6: true
websecure:
expose:
default: true
ipv6: true
service:
additionalServices:
ipv6:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/tke-existed-lbid: lb-xxx
Enable Gateway API
Gateway API support is not enabled by default. Enable it with the following configuration:
providers:
kubernetesGateway:
enabled: true
gateway:
enabled: false # Disable automatic creation of Gateway objects in the same namespace as Traefik, recommend creating manually as needed (one or more, can cross namespaces).
If you want to simultaneously disable Ingress and Traefik's own CRD support, use the following configuration:
providers:
kubernetesGateway:
enabled: true
kubernetesIngress:
enabled: false
kubernetesCRD:
enabled: false
Using Ingress to Manage Traffic
Traefik supports using Kubernetes Ingress resources as dynamic configuration. You can directly create Ingress resources in the cluster for external exposure, adding the specified IngressClass (customizable during Traefik installation, default is traefik). Example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: traefik
rules:
- host: traefik.demo.com
http:
paths:
- path: /test
backend:
serviceName: nginx
servicePort: 80
TKE has not yet productized Traefik, so you cannot directly create Ingress visually in the TKE console. You need to create using YAML.
Using Traefik CRD to Manage Traffic
Traefik not only supports standard Kubernetes Ingress resources but also Traefik-specific CRD resources like IngressRoute, which can support more advanced features that Ingress lacks. IngressRoute usage example:
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: test-ingressroute
spec:
entryPoints:
- web
routes:
- match: Host(`traefik.demo.com`) && PathPrefix(`/test`)
kind: Rule
services:
- name: nginx
port: 80
For more Traefik usage, refer to Traefik Official Documentation.
Using Gateway API to Manage Traffic
Traefik also supports Gateway API. If you enable Gateway API support, you can use the Gateway API approach to manage traffic. Examples below.
First create a Gateway object (defined ports automatically map to corresponding LoadBalancer Services, exposed through CLB listeners):
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: prod-gw
namespace: prod
spec:
gatewayClassName: traefik # Specify the automatically created GatewayClass name
listeners:
- name: http
protocol: HTTP
port: 8000
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
Then define forwarding rules (like HTTPRoute) and reference the Gateway object:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: foo
namespace: prod
spec:
parentRefs: # Reference Gateway object
- name: prod-gw
namespace: prod
hostnames:
- "foo.example.com"
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: foo
port: 8000