Egress Gateway Guide
Overview
This article explains how to use Cilium's Egress Gateway and CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy to flexibly control which egress IP is used for outbound traffic from the cluster.
Known Issues
Using Cilium's Egress Gateway feature has the following known issues:
- Egress policy delay for new Pods: After a new Pod starts, if it matches an Egress policy, the expectation is that the Pod's outbound traffic should go through the specified egress gateway. However, during the initial period after Pod startup, this policy may not take effect immediately, though this delay is typically very short and doesn't affect most scenarios.
- Incompatibility with Cilium's Cluster Mesh and CiliumEndpointSlice features.
Enabling Egress Gateway
To enable Egress Gateway, the following conditions must be met:
- Enable cilium to replace kube-proxy.
- Enable IP masquerade using BPF implementation instead of the default iptables implementation.
Method to enable Egress Gateway during cilium installation:
helm upgrade --install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace kube-system \
--set image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set operator.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/operator \
--set certgen.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/certgen \
--set hubble.relay.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-relay \
--set hubble.ui.backend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui-backend \
--set hubble.ui.frontend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui \
--set nodeinit.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/startup-script \
--set preflight.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set preflight.envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set clustermesh.apiserver.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/clustermesh-apiserver \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.agent.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-agent \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.server.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-server \
--set operator.tolerations[0].key="node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane",operator.tolerations[0].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[1].key="node-role.kubernetes.io/master",operator.tolerations[1].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[2].key="node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",operator.tolerations[2].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[3].key="node.cloudprovider.kubernetes.io/uninitialized",operator.tolerations[3].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[4].key="tke.cloud.tencent.com/uninitialized",operator.tolerations[4].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[5].key="tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip-unavailable",operator.tolerations[5].operator="Exists" \
--set routingMode=native \
--set endpointRoutes.enabled=true \
--set ipam.mode=delegated-plugin \
--set devices=eth+ \
--set cni.chainingMode=generic-veth \
--set cni.customConf=true \
--set cni.configMap=cni-config \
--set cni.externalRouting=true \
--set extraConfig.local-router-ipv4=169.254.32.16 \
--set localRedirectPolicies.enabled=true \
--set sysctlfix.enabled=false \
--set kubeProxyReplacement=true \
--set k8sServiceHost=$(kubectl get ep kubernetes -n default -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].ip}') \
--set k8sServicePort=60002 \
--set egressGateway.enabled=true \
--set enableIPv4Masquerade=true \
--set bpf.masquerade=true \
--set ipMasqAgent.enabled=true \
--set ipMasqAgent.config.masqLinkLocal=true
Then restart cilium components to take effect:
kubectl rollout restart ds cilium -n kube-system
kubectl rollout restart deploy cilium-operator -n kube-system
If you already installed cilium using the Install cilium using helm provided in Installing Cilium, the command to enable Egress Gateway can be simplified to:
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace kube-system \
--reuse-values \
--set egressGateway.enabled=true \
--set enableIPv4Masquerade=true \
--set bpf.masquerade=true \
--set ipMasqAgent.enabled=true \
--set ipMasqAgent.config.masqLinkLocal=true
Creating Egress Nodes
You can create a node pool as an Egress node pool, which can later be configured to route certain Pods' outbound traffic through these nodes. Refer to the Creating New Node Pool section in Installing Cilium for creation methods.
Things to note:
- Use the node pool to label the scaled-out nodes (e.g.,
egress-node=true) to identify them as Egress Gateway nodes. - If internet access is needed, assign public IPs to the nodes.
- To prevent regular Pods from being scheduled there, add taints.
- Egress node pools typically don't enable auto-scaling and set a fixed number of nodes.
Below are specific operational considerations for creating node pools:
- Native Node Pool
- Regular Node Pool
- Karpenter Node Pool
If creating through the console, make sure to check Create Elastic Public IP:

Add Labels and Taints (optional):

If creating via terraform, refer to the following code snippet:
resource "tencentcloud_kubernetes_native_node_pool" "cilium" {
name = "cilium"
cluster_id = tencentcloud_kubernetes_cluster.tke_cluster.id
type = "Native"
annotations {
name = "node.tke.cloud.tencent.com/beta-image"
value = "ts4-public"
}
# Label the scaled-out nodes with this label
labels {
name = "egress-node"
value = "true"
}
# (Optional) Add taints to nodes to prevent regular Pods from scheduling to Egress nodes
taints {
key = "egress-node"
effect = "NoSchedule"
value = "true"
}
native {
# Set egress node replica count
replicas = 1
internet_accessible {
# Pay by traffic
charge_type = "TRAFFIC_POSTPAID_BY_HOUR"
# Maximum outbound bandwidth 100Mbps
max_bandwidth_out = 100
}
# Omit other necessary but unrelated configurations
}
If creating through the console, make sure to check Assign Free Public IP:

Add Labels and Taints (optional):

If creating via terraform, refer to the following code snippet:
resource "tencentcloud_kubernetes_node_pool" "cilium" {
name = "cilium"
cluster_id = tencentcloud_kubernetes_cluster.tke_cluster.id
node_os = "img-gqmik24x" # TencentOS 4, currently requires whitelisting for regular node pools
enable_auto_scale = false # Disable auto-scaling
desired_capacity = 3 # Set egress node count
auto_scaling_config {
# Pay by traffic
internet_charge_type = "TRAFFIC_POSTPAID_BY_HOUR"
# Assign free public IP
internet_max_bandwidth_out = 100
# Assign free public IP
public_ip_assigned = true
# Omit other necessary but unrelated configurations
}
labels = {
# Label the scaled-out nodes with this label
"egress-node" = "true"
}
# (Optional) Add taints to nodes to prevent regular Pods from scheduling to Egress nodes
taints {
key = "egress-node"
effect = "NoSchedule"
value = "true"
}
Configure node public network in TKEMachineNodeClass, configure node Label in NodePool:
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: default
spec:
disruption:
consolidationPolicy: WhenEmptyOrUnderutilized
consolidateAfter: 5m
budgets:
- nodes: 10%
template:
metadata:
annotations:
beta.karpenter.k8s.tke.machine.spec/annotations: node.tke.cloud.tencent.com/beta-image=ts4-public
# Label the scaled-out nodes with this label
labels:
egress-node: "true"
# (Optional) Add taints to nodes to prevent regular Pods from scheduling to Egress nodes
taints:
- key: egress-node
effect: NoSchedule
value: "true"
spec:
requirements:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64"]
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values: ["linux"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.tke/instance-family
operator: In
values: ["S5", "SA2", "SA5"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["on-demand"]
- key: "karpenter.k8s.tke/instance-cpu"
operator: Gt
values: ["1"]
nodeClassRef:
group: karpenter.k8s.tke
kind: TKEMachineNodeClass
name: default
limits:
cpu: 100
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.tke/v1beta1
kind: TKEMachineNodeClass
metadata:
name: default
spec:
internetAccessible:
chargeType: TrafficPostpaidByHour # Pay by traffic
maxBandwidthOut: 100 # Maximum outbound bandwidth 100Mbps
subnetSelectorTerms:
- id: subnet-12sxk3z4
- id: subnet-b8qyi2dk
securityGroupSelectorTerms:
- id: sg-nok01xpa
sshKeySelectorTerms:
- id: skey-3t01mlvf
After the node pool is created and nodes are initialized, check which nodes are egress nodes and what public IPs are assigned using:
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide -l egress-node=true
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
172.22.48.125 Ready <none> 3h17m v1.32.2-tke.6 172.22.48.125 43.134.181.245 TencentOS Server 4.4 6.6.98-40.2.tl4.x86_64 containerd://1.6.9-tke.8
172.22.48.48 Ready <none> 3h17m v1.32.2-tke.6 172.22.48.48 43.156.74.191 TencentOS Server 4.4 6.6.98-40.2.tl4.x86_64 containerd://1.6.9-tke.8
172.22.48.64 Ready <none> 3h17m v1.32.2-tke.6 172.22.48.64 43.134.178.226 TencentOS Server 4.4 6.6.98-40.2.tl4.x86_64 containerd://1.6.9-tke.8
Configuring CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
By configuring CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy, you can flexibly define which egress IPs are used for which Pods' traffic leaving the cluster. Refer to the official documentation Writing egress gateway policies for configuration methods.
Usage Examples
Outbound Traffic Through Fixed Egress Nodes
If you want outbound traffic to go through fixed Egress nodes (when accessing the internet, the source IP will be fixed to the public IP bound to the Egress node), refer to the following configuration method.
Deploy an nginx workload:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
Configure CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy to specify that this workload uses a specific egress node for internet access:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector: # Specify which Pods this egress policy applies to
matchLabels:
app: nginx # Specify Pods with app=nginx label
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: default # Specify default namespace
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway:
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.119 # egress node name
# Important: Testing shows that in TKE environment, the internal IP of the egress node must be specified here,
# used to determine the source IP when the egress node forwards outbound traffic. Whether forwarding internal
# or public network traffic, the source IP used when leaving the egress node is the node's internal IP.
egressIP: 172.22.49.119
Check the egress node:
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide 172.22.49.119
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
172.22.49.119 Ready <none> 69m v1.32.2-tke.6 172.22.49.119 129.226.84.9 TencentOS Server 4.4 6.6.98-40.2.tl4.x86_64 containerd://1.6.9-tke.8
You can see the node's public IP is 129.226.84.9. Enter the Pod to test the current egress IP:
$ kubectl -n default exec -it deployment/nginx -- curl ifconfig.me
129.226.84.9
The final egress IP is 129.226.84.9, which meets expectations.
Outbound Traffic Through a Group of Egress Nodes
If you want outbound traffic to go through a fixed group of Egress nodes (when accessing the internet, the source IP will be fixed to the public IP bound to the Egress node), refer to the following configuration method.
Deploy an nginx workload:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
Configure CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy to specify that this workload uses a group of Egress nodes for outbound traffic:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector: # Specify which Pods this egress policy applies to
matchLabels:
app: nginx # Specify Pods with app=nginx label
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: default # Specify namespace
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway: # This field is required. If you want to specify multiple egress nodes, you must still specify one here, otherwise it will error: spec.egressGateway: Required value
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.20 # egress node name
egressIP: 172.22.49.20 # egress node internal IP
egressGateways: # Add remaining egress nodes to this list
- nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.147
egressIP: 172.22.49.147
- nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.119
egressIP: 172.22.49.119
Testing shows that different Pods in the workload may use different egress public IPs:
$ kubectl get pods -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\n"}{end}' | xargs -I {} sh -c 'kubectl exec -n default -it {} -- curl -s ifconfig.me 2>/dev/null || echo "Failed"; printf ":\t%s\n" "{}"'
129.226.84.9: nginx-54c98b4f84-5wlpc
43.156.123.70: nginx-54c98b4f84-6jx8n
43.156.123.70: nginx-54c98b4f84-82wmq
129.226.84.9: nginx-54c98b4f84-8ptvh
129.226.84.9: nginx-54c98b4f84-jfr2x
129.226.84.9: nginx-54c98b4f84-jlrr7
43.156.123.70: nginx-54c98b4f84-mpvpz
129.226.84.9: nginx-54c98b4f84-s7q4s
43.156.123.70: nginx-54c98b4f84-vsnng
43.156.123.70: nginx-54c98b4f84-xt8bs
But all use the public IPs bound to the currently defined group of egress nodes:
$ kubectl get nodes -o custom-columns="NAME:.metadata.name,EXTERNAL-IP:.status.addresses[?(@.type=='ExternalIP')].address" -l egress-node=true
NAME EXTERNAL-IP
172.22.49.119 129.226.84.9
172.22.49.147 43.156.123.70
172.22.49.20 43.163.1.23
All Cluster Outbound Traffic Through Egress Nodes
If you want all Pods' outbound traffic in the cluster to go through Egress nodes, you can use podSelector: {} to select all cluster Pods:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector: {} # Select all cluster Pods
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway: # This field is required. If you want to specify multiple egress nodes, you must still specify one here, otherwise it will error: spec.egressGateway: Required value
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.20 # egress node name
egressIP: 172.22.49.20 # egress node internal IP
egressGateways: # Add remaining egress nodes to this list
- nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.147
egressIP: 172.22.49.147
- nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.119
egressIP: 172.22.49.119
Different Environments or Business Pods Using Different Egress Nodes
If different environments or business Pods are isolated by namespace, you can specify that Pods in a certain namespace use specific Egress nodes for outbound traffic:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: prod # Specify all Pods in prod namespace
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway:
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.119
egressIP: 172.22.49.119
If different businesses are distinguished by labels, you can specify that Pods with specific labels across all namespaces use specific Egress nodes for outbound traffic:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
business: mall # Specify all Pods with business=mall label
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway:
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: 172.22.49.119
egressIP: 172.22.49.119
FAQ
Network Connectivity Issues After Policy Configuration
First confirm if the CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy configuration method is correct. In TKE environment, ensure that egressGateway's nodeSelector only selects one node, and egressIP must be configured as that node's internal IP, otherwise connectivity issues may occur.
You can also log into the cilium pod on the egress node and execute cilium-dbg bpf egress list to view current egress bpf rules on the node:
$ kubectl -n kube-systme exec -it cilium-nz5hd -- bash
root@VM-49-119-tencentos:/home/cilium# cilium-dbg bpf egress list
Source IP Destination CIDR Egress IP Gateway IP
172.22.48.4 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.10 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.14 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.37 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.38 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.39 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.41 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.42 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.43 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.44 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.45 0.0.0.0/0 172.22.49.119 172.22.49.119
172.22.48.46 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
172.22.48.47 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 172.22.49.147
Source IP is the Pod IP, Egress IP is the source IP used when traffic goes through the current node, 0.0.0.0 means the current node is not forwarding traffic for the corresponding Pod IP. If all are 0.0.0.0, it means no egress rules are selecting the current node.
Unexpected Egress IP
Usually conflicts with NAT gateway. If the VPC routing table is configured to route public traffic through a NAT gateway, traffic may eventually go through the NAT gateway instead of using the public IP bound to the egress node. Check if the VPC routing table has routing rules configured to send traffic to the NAT gateway.
How to route outbound traffic through machines outside the VPC?
In certain specific scenarios, you may want some Pod outbound traffic to go through designated machines outside the VPC (for example, when the business egress IP is in another VPC, another cloud, or an IDC data center, and a third party has whitelisted that IP, making it inconvenient to change, so you need the outbound traffic to exit through the machine where this IP is located). However, when Cilium uses CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy to configure policies, it requires the Egress machine to be a node in the current cluster. Normally, nodes added to a TKE cluster are machines within the VPC. So how can you route outbound traffic through machines outside the VPC?
You can add machines outside the VPC to the TKE cluster as registered nodes, and then configure the egress gateway in CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy to be that node.
The specific steps are:
- Before installing Cilium, enable registered nodes first in the TKE cluster's basic information page, and check to enable dedicated line connection support (after enabling, the cluster's apiserver address will change, and since Cilium replaces kube-proxy, it needs to be aware of the apiserver address - this is why it should be enabled before installing Cilium).
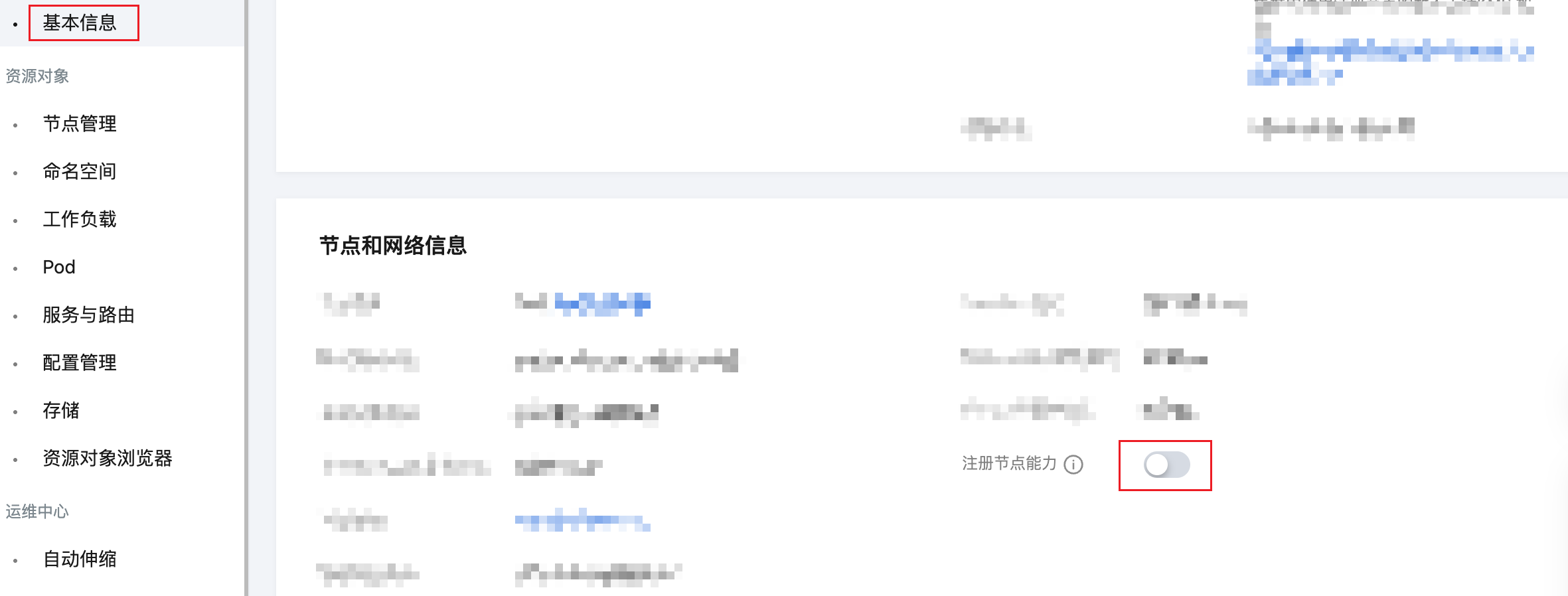
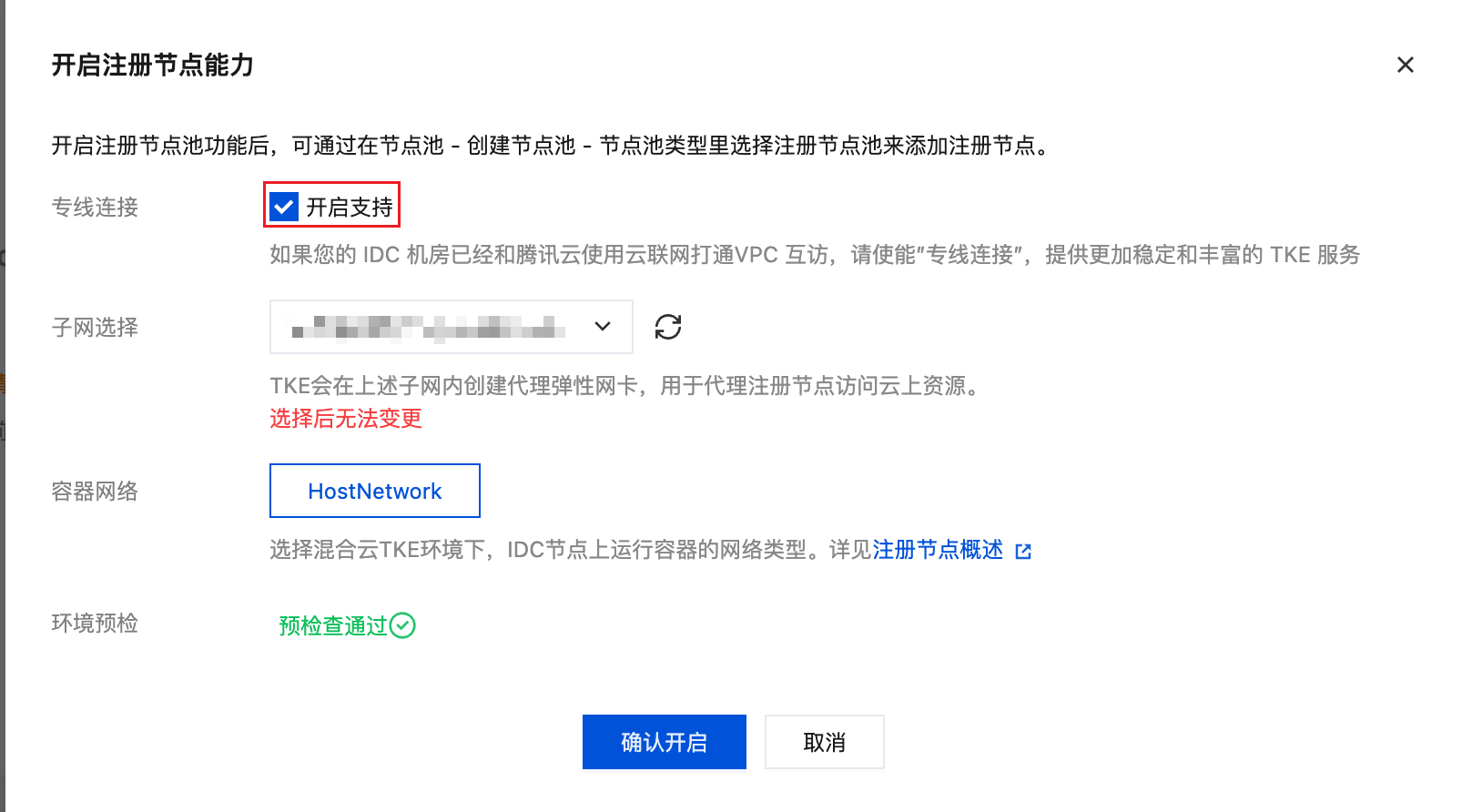
- Install Cilium and enable Egress Gateway.
- Prepare the Egress machine outside the VPC. The main requirements are that the network is connected to the VPC where the TKE cluster is located, and the Linux kernel version is >= 5.10.
- Create a new registered node pool. It's recommended to add both Labels and Taints (Taints example:
egress-node=true:NoSchedule, which prevents regular Pods from being scheduled to this node, because registered nodes cannot use the VPC-CNI network plugin, cannot be assigned Pod IPs, and can only use HostNetwork). - Enter the newly created registered node pool, click to create a new node, copy the registration script as prompted and execute it on the Egress machine outside the VPC to add that machine as a node to the TKE cluster.
- Configure CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy as needed to route specified outbound traffic through the machine outside the VPC. Example (Note that you need to replace the hostname and the egressIP):
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumEgressGatewayPolicy
metadata:
name: egress-test
spec:
selectors:
- podSelector: # Specify which Pods this egress policy applies to
matchLabels:
app: nginx # Specify Pods with the app=nginx label
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: test # Specify the test namespace
destinationCIDRs:
- "0.0.0.0/0"
- "::/0"
egressGateway:
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/hostname: node-10.111.128.148 # Egress registered node name
# Important: Testing shows that in TKE environments, you must specify the egress node's
# internal IP here. This determines what source IP the egress node uses when forwarding
# outbound traffic. Whether forwarding internal or public network traffic, the source IP
# when leaving the egress node is the node's internal IP.
egressIP: 10.111.128.148