Installing Cilium
This article describes how to install Cilium in a TKE cluster.
Prerequisites
Prepare TKE Cluster
Installing Cilium is a significant change to the cluster. It is not recommended to install it in a cluster with production workloads running, as the installation process may affect the normal operation of online services. It is recommended to install Cilium in a newly created TKE cluster.
Create a TKE cluster in the Container Service Console, paying attention to the following key options:
- Cluster Type: Standard Cluster
- Kubernetes Version: No lower than 1.30.0, recommended to choose the latest version (refer to Cilium Kubernetes Compatibility).
- Operating System: TencentOS 4 or Ubuntu >= 22.04.
- Container Network Plugin: VPC-CNI shared NIC multi-IP.
- Nodes: Do not add any regular nodes or native nodes to the cluster before installation to avoid residual rules and configurations. Add them after the installation is complete.
- Basic Components: Uncheck ip-masq-agent to avoid conflicts.
- Enhanced Components: If you want to use Karpenter node pools, check to install the Karpenter component; otherwise, no need to check (refer to the node pool selection section later).
After the cluster is successfully created, you need to enable cluster access to expose the cluster's apiserver so that the helm command can operate the TKE cluster normally when installing Cilium later. Refer to How to Enable Cluster Access.
Depending on your situation, choose to enable internal network access or public network access, mainly depending on whether the network where the helm command is located can communicate with the VPC where the TKE cluster is located:
- If it can communicate, enable internal network access.
- If it cannot communicate, enable public network access. Currently, enabling public network access requires deploying the
kubernetes-proxycomponent to the cluster as a relay, which depends on the existence of nodes in the cluster (this dependency may be removed in the future, but currently it is required). If you want to use public network access, it is recommended to add a super node to the cluster first so that thekubernetes-proxypod can be scheduled normally, and then delete this super node after Cilium installation is complete.
If using Terraform to create a cluster, refer to the following code snippet:
resource "tencentcloud_kubernetes_cluster" "tke_cluster" {
# Standard Cluster
cluster_deploy_type = "MANAGED_CLUSTER"
# Kubernetes Version >= 1.30.0
cluster_version = "1.32.2"
# Operating System, TencentOS 4 image ID, currently requires submitting a ticket to apply for using this image
cluster_os = "img-gqmik24x"
# Container Network Plugin: VPC-CNI
network_type = "VPC-CNI"
# Enable Cluster APIServer Access
cluster_internet = true
# Expose APIServer through internal CLB, need to specify the subnet ID where CLB is located
cluster_intranet_subnet_id = "subnet-xxx"
# Do not install ip-masq-agent (disable_addons requires tencentcloud provider version 1.82.33+)
disable_addons = ["ip-masq-agent"]
# To use the Karpenter node pool, the Karpenter component must be installed. (cluster-autoscaler and karpenter are mutually exclusive,
# enabling this component will prevent cluster-autoscaler from being installed, thus disabling the scaling functionality of the native
# node pool and the regular node pool, if you are not using a Karpenter node pool, you can omit the following code. For specific node
# pool selection, please refer to the section on "Create New Node Pools" below).
extension_addon {
name = "karpenter"
param = jsonencode({
"kind" : "App", "spec" : { "chart" : { "chartName" : "karpenter" } }
})
}
# Omit other necessary but unrelated configurations
}
Prepare Helm Environment
- Ensure helm and kubectl are installed and configured with a kubeconfig that can connect to the cluster (refer to Connecting to Cluster).
- Add Cilium's helm repo:
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/
Install Cilium
Configure CNI
Prepare the CNI configuration ConfigMap cni-config.yaml for Cilium:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cni-config
namespace: kube-system
data:
cni-config: |-
{
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"name": "generic-veth",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "tke-route-eni",
"routeTable": 1,
"disableIPv6": true,
"mtu": 1500,
"ipam": {
"type": "tke-eni-ipamc",
"backend": "127.0.0.1:61677"
}
},
{
"type": "cilium-cni",
"chaining-mode": "generic-veth"
}
]
}
Create the CNI ConfigMap:
kubectl apply -f cni-config.yaml
Install Cilium using Helm
Execute the installation using Helm:
k8sServiceHost is the apiserver address, obtained dynamically through command.
helm upgrade --install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace kube-system \
--set image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set operator.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/operator \
--set certgen.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/certgen \
--set hubble.relay.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-relay \
--set hubble.ui.backend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui-backend \
--set hubble.ui.frontend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui \
--set nodeinit.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/startup-script \
--set preflight.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set preflight.envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set clustermesh.apiserver.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/clustermesh-apiserver \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.agent.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-agent \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.server.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-server \
--set operator.tolerations[0].key="node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane",operator.tolerations[0].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[1].key="node-role.kubernetes.io/master",operator.tolerations[1].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[2].key="node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",operator.tolerations[2].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[3].key="node.cloudprovider.kubernetes.io/uninitialized",operator.tolerations[3].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[4].key="tke.cloud.tencent.com/uninitialized",operator.tolerations[4].operator="Exists" \
--set operator.tolerations[5].key="tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip-unavailable",operator.tolerations[5].operator="Exists" \
--set routingMode=native \
--set endpointRoutes.enabled=true \
--set ipam.mode=delegated-plugin \
--set enableIPv4Masquerade=false \
--set devices=eth+ \
--set cni.chainingMode=generic-veth \
--set cni.customConf=true \
--set cni.configMap=cni-config \
--set cni.externalRouting=true \
--set extraConfig.local-router-ipv4=169.254.32.16 \
--set localRedirectPolicies.enabled=true \
--set sysctlfix.enabled=false \
--set kubeProxyReplacement=true \
--set k8sServiceHost=$(kubectl get ep kubernetes -n default -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].ip}') \
--set k8sServicePort=60002
The following is the values.yaml containing explanations for each parameter:
- TKE Adaptation Related
- Image Related
# Use native routing, Pods directly use VPC IP routing without overlay, refer to native routing: https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/routing/#native-routing
routingMode: "native"
endpointRoutes:
# When using native routing, this option must be set to true. Indicates that when forwarding Pod traffic, it routes directly to veth devices without going through cilium_host network card
enabled: true
ipam:
# TKE Pod IP allocation is handled by tke-eni-ipamd component, cilium does not need to handle Pod IP allocation
mode: "delegated-plugin"
# No IP masquerade needed when using VPC-CNI
enableIPv4Masquerade: false
# In TKE nodes, eth-prefixed network cards may have incoming/outgoing traffic (Pod traffic goes through auxiliary network cards, eth1, eth2 ...), use this parameter to mount cilium ebpf programs on all eth-prefixed network cards,
# so that packets can be properly reverse NAT based on conntrack, otherwise it may cause network connectivity issues in some scenarios (such as cross-node HostPort access)
devices: eth+
cni:
# Use generic-veth for CNI Chaining with VPC-CNI, refer to: https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/installation/cni-chaining-generic-veth/
chainingMode: generic-veth
# CNI configuration is fully customized
customConf: true
# Name of the ConfigMap storing CNI configuration
configMap: cni-configuration
# VPC-CNI will automatically configure Pod routing, cilium doesn't need to configure it
externalRouting: true
operator:
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane"
operator: Exists
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: Exists
- key: "node.kubernetes.io/not-ready"
operator: Exists
- key: "node.cloudprovider.kubernetes.io/uninitialized"
operator: Exists
# Tolerate TKE's taints to avoid circular dependencies during first installation
- key: "tke.cloud.tencent.com/uninitialized"
operator: Exists
- key: "tke.cloud.tencent.com/eni-ip-unavailable"
operator: Exists
extraConfig:
# cilium doesn't handle Pod IP allocation, need to manually specify an IP address that won't conflict, as the IP address for cilium_host virtual network card on each node
local-router-ipv4: 169.254.32.16
# Enable CiliumLocalRedirectPolicy capability, refer to https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/kubernetes/local-redirect-policy/
localRedirectPolicies:
enabled: true
# Disable sysctlfix to prevent restarting systemd-sysctl from resetting eth0's rp_filter to 1, which could cause network unavailable in some scenarios.
sysctlfix:
enabled: false
# Replace kube-proxy, including ClusterIP forwarding, NodePort forwarding, plus HostPort forwarding capability
kubeProxyReplacement: "true"
# Note: Replace with actual apiserver address, obtain method: kubectl get ep kubernetes -n default -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].ip}'
k8sServiceHost: 169.254.128.112
k8sServicePort: 60002
Replace all cilium dependent images with mirror images that can be directly pulled from internal network in TKE environment, avoiding image pull failures due to network issues:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium
envoy:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy
operator:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/operator
certgen:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/certgen
hubble:
relay:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-relay
ui:
backend:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui-backend
frontend:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui
nodeinit:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/startup-script
preflight:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium
envoy:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy
clustermesh:
apiserver:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/clustermesh-apiserver
authentication:
mutual:
spire:
install:
agent:
image:
repository: docker.io/k8smirror/spire-agent
server:
image:
repository: docker.io/k8smirror/spire-server
For production environment deployment, it's recommended to save parameters to YAML files, then execute commands similar to the following during installation or update (if upgrading version, just replace --version):
helm upgrade --install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace=kube-system \
-f tke-values.yaml \
-f image-values.yaml
If you have many custom configurations, it's recommended to split them into multiple yaml files for maintenance, for example, put configurations for enabling Egress Gateway in egress-values.yaml, put container request and limit configurations in resources-values.yaml, and merge multiple yaml files by adding multiple -f parameters when updating configurations:
helm upgrade --install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace=kube-system \
-f tke-values.yaml \
-f image-values.yaml \
-f egress-values.yaml \
-f resources-values.yaml
Ensure cilium related pods are running normally:
$ kubectl --namespace=kube-system get pod -l app.kubernetes.io/part-of=cilium
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cilium-5rfrk 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-9mntb 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-envoy-4r4x9 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-envoy-kl5cz 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-envoy-sgl5v 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-operator-896cdbf88-jlgt7 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-operator-896cdbf88-nj6jc 1/1 Running 0 1m
cilium-zrxwn 1/1 Running 0 1m
Uninstall TKE Components
Use kubectl patch to uninstall tke-cni-agent and kube-proxy:
kubectl -n kube-system patch daemonset kube-proxy -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"nodeSelector":{"label-not-exist":"node-not-exist"}}}}}'
kubectl -n kube-system patch daemonset tke-cni-agent -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"nodeSelector":{"label-not-exist":"node-not-exist"}}}}}'
- By adding nodeSelector to make daemonset not deploy to any nodes, equivalent to uninstalling, while also providing a fallback option; currently kube-proxy can only be uninstalled this way, if directly deleting kube-proxy, subsequent cluster upgrades will be blocked.
- Using a VPC-CNI network with a fully customized CNI configuration, tke-cni-agent can be dispensed with and uninstalled to avoid CNI profile conflicts.
- As mentioned earlier, it's not recommended to add nodes before installing cilium. If regular nodes or native nodes were added before cilium installation for some reason, the existing node needs to be restarted to avoid leaving any related rules and configurations.
- If you forgot to uncheck ip-masq-agent when creating the cluster, you can uninstall it manually:
kubectl -n kube-system patch daemonset ip-masq-agent -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"nodeSelector":{"label-not-exist":"node-not-exist"}}}}}'
Configuring APF Rate Limiting
Cilium-agent runs on each node. When the cluster scale is large, it may put significant pressure on the APIServer. In extreme scenarios, this could cause a cascade failure, making the entire cluster unavailable. Therefore, it's necessary to configure APF to rate limit Cilium's components.
Save the following content to the file cilium-apf.yaml:
You can modify the value of nominalConcurrencyShares according to the cluster specifications, refer to the comments.
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1
kind: FlowSchema
metadata:
name: cilium
spec:
distinguisherMethod:
type: ByUser
matchingPrecedence: 2
priorityLevelConfiguration:
name: cilium
rules:
- resourceRules:
- apiGroups:
- 'cilium.io'
clusterScope: true
namespaces:
- '*'
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- list
- apiGroups:
- ''
clusterScope: true
namespaces:
- '*'
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- list
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
serviceAccount:
name: cilium
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1
kind: PriorityLevelConfiguration
metadata:
name: cilium
spec:
limited:
# L500=10, L1000=6, L3000=3, L5000=2
nominalConcurrencyShares: 2
borrowingLimitPercent: 0
lendablePercent: 0
limitResponse:
queuing:
handSize: 6
queueLengthLimit: 50
queues: 64
type: Queue
type: Limited
Create APF rate limiting rules:
kubectl apply -f cilium-apf.yaml
Create New Node Pools
Node Pool Selection
The following three types of node pools can adapt to cilium:
- Native Node Pool: Based on native nodes, native nodes have rich features and are also the recommended node type for TKE (refer to Native Nodes vs Regular Nodes), OS fixed to use TencentOS.
- Regular Node Pool: Based on regular nodes (CVM), OS images are more flexible.
- Karpenter Node Pool: Similar to native node pool, based on native nodes, OS fixed to use TencentOS, but uses the more powerful Karpenter for node management instead of cluster-autoscaler (CA) used by regular node pools and native node pools.
The following is a comparison of these node pool types, choose the appropriate node pool type based on your situation:
| Node Pool Type | Node Type | Available OS Images | Node Scaling Component |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Node Pool | Native Nodes | TencentOS | cluster-autoscaler |
| Regular Node Pool | Regular Nodes (CVM) | Ubuntu/TencentOS/Custom Images | cluster-autoscaler |
| Karpenter Node Pool | Native Nodes | TencentOS | Karpenter |
Below are the steps to create various node pools.
Create Karpenter Node Pool
Before creating a Karpenter node pool, ensure the Karpenter component is enabled, refer to tke-karpenter instructions.
Prepare nodepool.yaml for configuring Karpenter node pool, here's an example:
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: default
spec:
disruption:
consolidationPolicy: WhenEmptyOrUnderutilized
consolidateAfter: 5m
budgets:
- nodes: 10%
template:
metadata:
annotations:
# Native nodes default to installing TencentOS 3, which is incompatible with the latest cilium version, specify this annotation to install TencentOS 4
# Note: Currently using this system image still requires submitting a ticket to apply
beta.karpenter.k8s.tke.machine.spec/annotations: node.tke.cloud.tencent.com/image-label=ts4-public
spec:
requirements:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64"]
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values: ["linux"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.tke/instance-family
operator: In
# Specify the expected instance type list, you can first confirm which instance types are actually available in the cluster's region and related availability zones in the console
# Complete list reference: https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/213/11518#INSTANCETYPE
values: ["S5", "SA2"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["on-demand"]
- key: "karpenter.k8s.tke/instance-cpu"
operator: Gt
values: ["1"] # Specify the minimum CPU cores when scaling up
nodeClassRef:
group: karpenter.k8s.tke
kind: TKEMachineNodeClass
name: default # Reference TKEMachineNodeClass
limits:
cpu: 100 # Limit the maximum CPU cores for the node pool
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.tke/v1beta1
kind: TKEMachineNodeClass
metadata:
name: default
spec:
subnetSelectorTerms: # VPC subnet where nodes belong
- id: subnet-12sxk3z4
- id: subnet-b8qyi2dk
securityGroupSelectorTerms: # Security groups bound to nodes
- id: sg-nok01xpa
sshKeySelectorTerms: # SSH keys bound to nodes
- id: skey-3t01mlvf
Create Karpenter node pool:
kubectl apply -f nodepool.yaml
Create Native Node Pool
The following are the steps to create a native node pool through the Container Service Console:
- In the cluster list, click the cluster ID to enter the cluster details page.
- Select Node Management from the left menu bar, click Node Pools to enter the node pool list page.
- Click Create New.
- Select Native Nodes.
- In Advanced Settings under Annotations, click Add:
node.tke.cloud.tencent.com/image-label=ts4-public(native nodes default to using TencentOS 3.1, which is incompatible with the latest cilium version, specify this annotation to make native nodes use TencentOS 4). - Choose other options according to your needs.
- Click Create Node Pool.
If you want to create a native node pool through terraform, refer to the following code snippet:
resource "tencentcloud_kubernetes_native_node_pool" "cilium" {
name = "cilium"
cluster_id = tencentcloud_kubernetes_cluster.tke_cluster.id
type = "Native"
annotations { # Add annotation to specify native nodes use TencentOS 4 to be compatible with cilium, currently using this system image still requires submitting a ticket to apply
name = "node.tke.cloud.tencent.com/image-label"
value = "ts4-public"
}
}
Create Regular Node Pool
The following are the steps to create a regular node pool through the Container Service Console:
- In the cluster list, click the cluster ID to enter the cluster details page.
- Select Node Management from the left menu bar, click Node Pools to enter the node pool list page.
- Click Create New.
- Select Regular Nodes.
- Operating System select TencentOS 4, Ubuntu 22.04 or Ubuntu 24.04.
- Choose other options according to your needs.
- Click Create Node Pool.
If you want to create a regular node pool through terraform, refer to the following code snippet:
resource "tencentcloud_kubernetes_node_pool" "cilium" {
name = "cilium"
cluster_id = tencentcloud_kubernetes_cluster.tke_cluster.id
node_os = "img-gqmik24x" # TencentOS 4 image ID, currently using this system image still requires submitting a ticket to apply
}
FAQ
How to view all default installation configurations for Cilium?
Cilium's helm installation package provides a large number of custom configuration items. The above installation steps only provide the necessary configurations for installing Cilium in TKE environment. In practice, you can adjust more configurations according to your needs.
Execute the following command to view all installation configuration items:
helm show values cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1
Why add local-router-ipv4 configuration?
Cilium will create a cilium_host virtual network card on each node and needs to configure an IP address. Since we want Cilium to coexist with TKE VPC-CNI network plugin, IP allocation needs to be handled by TKE VPC-CNI plugin, so Cilium doesn't handle IP allocation. Therefore, we need to manually specify an IP address that won't conflict through the local-router-ipv4 parameter. The IP address 169.254.32.16 won't conflict with other IPs on TKE, so this IP address is specified.
What to do if unable to connect to Cilium's helm repo?
When using helm to install Cilium, helm will get chart related information from Cilium's helm repo and download it. If unable to connect, it will report an error.
The solution is to download the chart compressed package in an environment that can connect:
$ helm pull cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1
$ ls cilium-*.tgz
cilium-1.19.1.tgz
Then copy the chart compressed package to the machine where helm installation is executed, and specify the path of the chart compressed package during installation:
helm upgrade --install cilium ./cilium-1.19.1.tgz \
--namespace kube-system \
-f values.yaml
How to optimize for large-scale scenarios?
If the cluster scale is large, it's recommended to enable the CiliumEndpointSlice feature. This feature was introduced in version 1.11 and is still in Beta stage in the current version (1.19.1) (see CiliumEndpointSlice Graduation to Stable). In large-scale scenarios, this feature can significantly improve Cilium performance and reduce apiserver pressure.
It's not enabled by default. The enablement method is to add the --set ciliumEndpointSlice.enabled=true parameter when using helm to install Cilium.
Can Global Router network mode clusters be installed?
Test conclusion: No.
It should be that Cilium doesn't support bridge CNI plugin (Global Router network plugin is based on bridge CNI plugin), related issues:
Can DataPlaneV2 be checked?
Conclusion: No.
When selecting VPC-CNI network plugin, there's a DataPlaneV2 option:
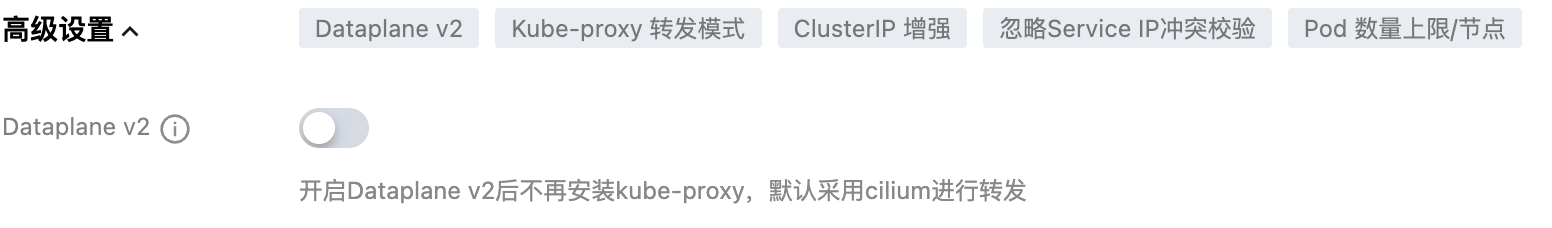
After checking, Cilium components will be deployed to the cluster (replacing kube-proxy components). If you install Cilium yourself again, it will cause conflicts. Moreover, the OS used by DataPlaneV2 is incompatible with the latest version of Cilium, so this option cannot be checked.
How can Pods access the public network?
You can create a public NAT gateway, then create new routing rules in the routing table of the VPC where the cluster is located, redirecting traffic accessing the external network to the public NAT gateway, and ensure the routing table is associated with the subnets used by the cluster. Refer to Accessing External Network through NAT Gateway.
If the node itself has public network bandwidth and you want Pods to directly utilize the node's public network capability to access the public network, you need to enable Cilium's IP Masquerade capability. For specific methods, refer to Configuring IP Masquerading.
If you have more advanced traffic egress requirements (such as specifying certain Pods to use a specific public IP to access the public network), you can refer to Egress Gateway Application Practice.
Image pull failure?
Most of the images that Cilium depends on are on quay.io. If you don't use the parameter configuration for replacing image addresses provided in this article during installation, it may cause Cilium related image pull failures (for example, if nodes don't have public network access capability, or the cluster is in mainland China).
In TKE environment, the mirror repository address quay.tencentcloudcr.com is provided for downloading images under the quay.io domain. Simply replace the quay.io domain in the original image address with quay.tencentcloudcr.com. Pulling goes through internal network, nodes don't need public network capability, and there are no regional restrictions.
If you configure more installation parameters, it may involve more image dependencies. If you don't configure image address replacement, it may cause image pull failures. Use the following command to replace all Cilium dependent images with mirror repository addresses that can be directly pulled from internal network in TKE environment:
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace kube-system \
--reuse-values \
--set image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set operator.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/operator \
--set certgen.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/certgen \
--set hubble.relay.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-relay \
--set hubble.ui.backend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui-backend \
--set hubble.ui.frontend.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui \
--set nodeinit.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/startup-script \
--set preflight.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium \
--set preflight.envoy.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy \
--set clustermesh.apiserver.image.repository=quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/clustermesh-apiserver \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.agent.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-agent \
--set authentication.mutual.spire.install.server.image.repository=docker.io/k8smirror/spire-server
If you use yaml to manage configurations, you can save the image replacement configuration to image-values.yaml:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium
envoy:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy
operator:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/operator
certgen:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/certgen
hubble:
relay:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-relay
ui:
backend:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui-backend
frontend:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/hubble-ui
nodeinit:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/startup-script
preflight:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium
envoy:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/cilium-envoy
clustermesh:
apiserver:
image:
repository: quay.tencentcloudcr.com/cilium/clustermesh-apiserver
authentication:
mutual:
spire:
install:
agent:
image:
repository: docker.io/k8smirror/spire-agent
server:
image:
repository: docker.io/k8smirror/spire-server
When updating Cilium, add a -f image-values.yaml to include the image replacement configuration:
helm upgrade --install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.19.1 \
--namespace=kube-system \
-f values.yaml \
-f image-values.yaml
Using the mirror repository address provided by TKE to pull external images itself doesn't provide SLA guarantee. Sometimes it may also fail to pull, but usually it will automatically retry and succeed eventually.
If you want image pulling to have higher availability, you can use TCR to host Cilium images to synchronize Cilium dependent images to your own TCR image repository, then refer to the dependent image replacement configuration here, and replace the corresponding images with your own synchronized image addresses.
Unable to use TencentOS 4?
TencentOS 4 system image is currently in internal testing and requires submitting a ticket to apply.
If not applied, adding regular nodes will not be able to select TencentOS 4 system image. If native nodes specify annotation to use TencentOS 4, the nodes will not be able to initialize successfully.
cilium-operator cannot become ready on super nodes?
cilium-operator uses hostNetwork and configures readiness probes. When using hostNetwork on super nodes, probe requests cannot connect, so cilium-operator cannot become ready.
It's not recommended to use super nodes in clusters where Cilium is installed. They can be removed. If you must use them, you can add taints to super nodes, and then add corresponding tolerations to Pods that need to be scheduled to super nodes.
cilium-agent connecting to apiserver reports operation not permitted error?
If when installing Cilium, k8sServiceHost points to a CLB address (the CLB used when enabling cluster internal network access), which is either a CLB VIP or a domain name that ultimately resolves to a CLB VIP, then the connection path from cilium-agent to apiserver will be intercepted and forwarded by Cilium itself, not actually going through CLB forwarding. Cilium's forwarding of this address is ultimately implemented by eBPF programs, and the eBPF program forwarding of this address is based on eBPF data (endpoint list) stored in the kernel. Under certain triggering conditions, the eBPF data may be refreshed, and the refresh may cause the endpoint list to be temporarily cleared. Once cleared, cilium-agent can no longer connect to apiserver (reporting operation not permitted error), and thus cannot perceive the current real endpoint list to update the eBPF data, forming a circular dependency. Normal operation is only restored after restarting the node.
Therefore, the recommendation is not to configure k8sServiceHost with the apiserver's CLB address, but to use the cluster's 169.254.x.x apiserver address (kubectl get ep kubernetes -n default -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].ip}'). This address is also a VIP, but it will not be intercepted and forwarded by Cilium, and it will never change after the cluster is created, so it can be safely used as the k8sServiceHost configuration. If you want to use a more recognizable domain name configuration, you can also resolve the domain name to this address and then configure it to k8sServiceHost.